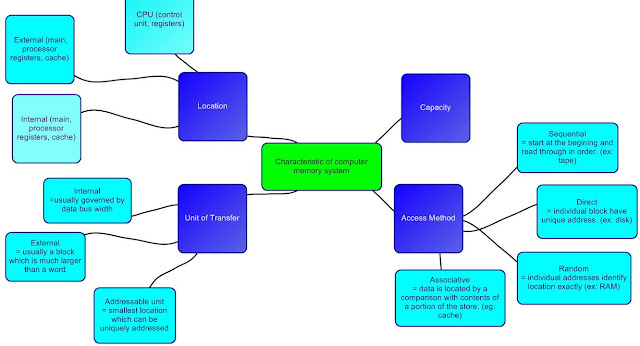
1.) 8 Characteristic of Computer Memory Systems
2.) Memory Hierarchy
3.) Semiconductor Memory Types
a.) Read/ Write memory
i.) DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory)
- bits stored as charge in capacitors.
- charges leak.
- need refreshing even when powered.
- bits stored as charge in capacitors.
- charges leak.
- need refreshing even when powered.
ii.) SRAM
(Static Random Access Memory)
- bit stored as on/off switches.
- no charges to leak.
- no refreshing needed when powered.
- bit stored as on/off switches.
- no charges to leak.
- no refreshing needed when powered.
b.) Read Only memory (ROM)
i.) PROM (Programmable Read-Only Memory)
- can be programmed only ONCE.
- nonvolatile, writing process performed electrically at a time
later.
- can be programmed only ONCE.
- nonvolatile, writing process performed electrically at a time
later.
ii.) EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory)
- erased by UV and can be altered many times.
- before write, all must be erased.
- erased by UV and can be altered many times.
- before write, all must be erased.
iii.) EEROM (Electrically Erasable Read-Only Memory)
- write at anytime without erasing prior contents electrically.
- location can be selectively erased and programmed.
- write at anytime without erasing prior contents electrically.
- location can be selectively erased and programmed.
iv.) Flash Memory
- a special type of EEPROM.
- erase whole memory electrically, per block or per chip erasable.
- a special type of EEPROM.
- erase whole memory electrically, per block or per chip erasable.
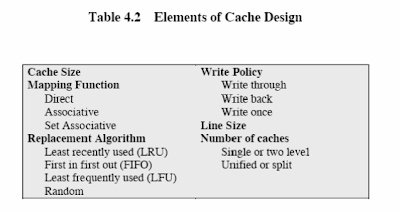
4.) Cache
- small amount of fast memory.
- Immediate buffer between normal main memory and CPU.
- may be located on CPU chip or module
- Immediate buffer between normal main memory and CPU.
- may be located on CPU chip or module
Cache operation
a.) CPU requests contents of memory location.b.) check cache for this data.
c.) if present, get from cache (fast) = Cache Hit.
d.) if not present, read required block from main memory to cache = Cache Miss.
e.) then deliver from a cache to CPU.
f.) cache include tags to identify which block of main memory is in each cache slot.
Direct, Associative and Set Associative Mapping
Cache Replacement
- When the address accessed by CPU is
not in cache, access has to be made to main memory.
- Along with the required word, the entire block is transferred to cache.
- But if cache is full, some existing cache memory is deleted to create space for the new entry.
- So some replacement algorithm is needed.
- Along with the required word, the entire block is transferred to cache.
- But if cache is full, some existing cache memory is deleted to create space for the new entry.
- So some replacement algorithm is needed.
5.) Cache Write Policy
= must not overwrite a cache block unless main memory is up to date.
Two cases to consider when block that is in
cache needs to be updated:
a.) Write through
= write the result in both the main memory and cache.
a.) Write through
= write the result in both the main memory and cache.
b.) Write back
= write in cache memory only to minimize memory writes.
= write in cache memory only to minimize memory writes.
6.) Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS)
- CMOS memory requires very little power
to retain its contents. Usually powered by a battery.
- CMOS stores vital data about the configuration of the computer system, even when the computer is turned off.
- CMOS stores vital data about the configuration of the computer system, even when the computer is turned off.
7.)Types of External Memory
a.) Magnetic Disk
- RAID
- Removable (floppy)
- RAID
- Removable (floppy)
b.) Optical
- CD-ROM
- CD-Recordable (CD-R)
- CD-R/W
- DVD
- CD-ROM
- CD-Recordable (CD-R)
- CD-R/W
- DVD
By Teoh Soon Gi